| International school of sport and leisure infrastructure management |
Educational program for planning, building, management, maintenance and usage of sport and leisure infrastructure |
Sport and Leisure
Sport and leisure are important part of life, school education, economy and World globalization. The number of sport and leisure programs has risen over the past decades. Many institutions, companies and people are involved in these programs. Schools provide physical education and sport competitions for children and youth. Adult people participate in sport for all. Professional sport has evolved into a major economic sector. It is accompanied by huge media coverage and marketing of goods and services. Sports tourism has developed. Olympic Games, international leagues and championships are part of the World globalization.
Leisure is an essential, integral part of modern urban life. It covers a wide range of programs and services. It includes tourist, recreational, fitness and wellness services, programs for body care, healthy living, children, women, elderly people and special programs. Leisure has become business activity, which is heavily advertised in the media. The sector is developing rapidly with the mass consumption of goods and services that are marketed worldwide.
Some business schools and experts, include event management, sport and tourist agencies, media, telecommunications, advertising, public relations, financial, insurance, health and other services and goods, in the sector of sport and leisure.
Infrastructure
Sport and leisure infrastructure encompasses facilities, systems, goods and services that enable the sport and leisure. Municipal infrastructure, water and energy supply systems, transport, communications, security and other systems which provide goods and services for the operations and maintenance, are parts of the infrastructure. There are several hundreds different types of sport and leisure facilities: sports centers and parks, recreational areas, baths and swimming pools, athletic and football stadiums, sports halls, skating rinks, tennis courts, ski resorts, golf courses, cycling tracks, horse racing facilities, shooting ranges and other facilities and areas. There are several hundred thousands big and several millions small sport centers and tourist centers, with facilities for sport and leisure, worldwide.
Some professional institutions include design, construction, management and maintenance of the sport and leisure infrastructure, production and trade of equipment and requisites, in the sector.
Economic sector of sport, leisure and infrastructure create several hundred billions of euros of annual turnover and represents 5% to 10% of Gross Domestic Product, in some countries and regions.
Environment
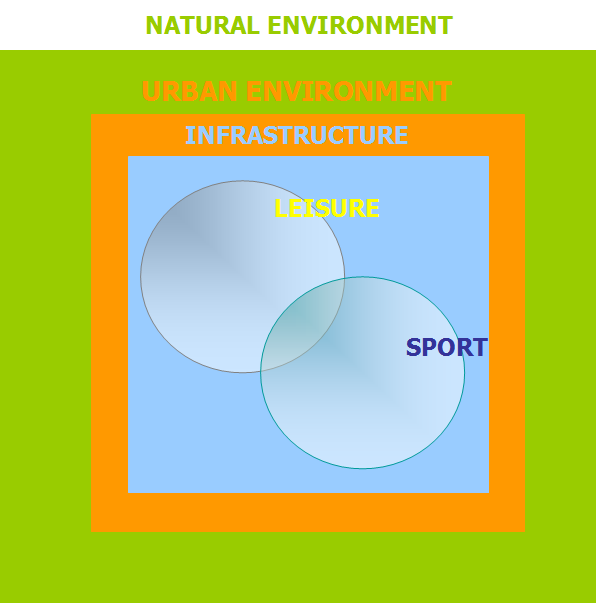
Important changes that define the future of sport and leisure infrastructure, have already occurred. They have started decades ago, advanced very quickly and in ever-increasing extent.
Natural resources (land, air, water, energy, biodiversity) are changing rapidly. The quality of natural resources is more and more aggravated, their consumption is too big and some are disappearing. Thousands of new sport centers are using huge areas, represent enormous consumption of water, energy and other natural resources and contribute to faster environmental changes.
Scheme 1: Environment and sport, leisure and infrastructure
 Interests
Interests are constantly developing and changing. We divide them into three large groups: (1) public interest, (2) private interests and (3) public-private partnership, which are reflected in new forms of social management. Interests of civil society (associations) are present in all three groups.
Public interests in the field of infrastructure, sport and leisure, are the largest and most important for regulating the sector and its future development. Contents of the public interests are: (1) sustainable development of infrastructure, sports and leisure, (2) availability of programs and services for all people, (3) increasing the quality of programs and services, (4) safety, (5) efficient management of public infrastructure and programs that are financed from public funds and (6) control of public funding.
Private sector interests are: (1) business sustainability, (2) development of new programs and services and their competitiveness in the markets, (3) successful marketing, (4) making profit and (5) high return on capital investments.
Public-private partnership is an area that is developing. Partnership has not yet been fully developed and regulated by law. It includes social management, which is pursuing both public and private interests in the infrastructure, sports and leisure.
Scheme 2: Interests in the sport, leisure and infrastructure

Interested parties
Sport, leisure and infrastructure, have become an important economic sector that generates hundreds of billions euro turnover and has millions of employees, worldwide. Sector is divided into public and private sector and social management, which combines the two previous.
Scheme 3: Interested parties in sport, leisure and infrastructure 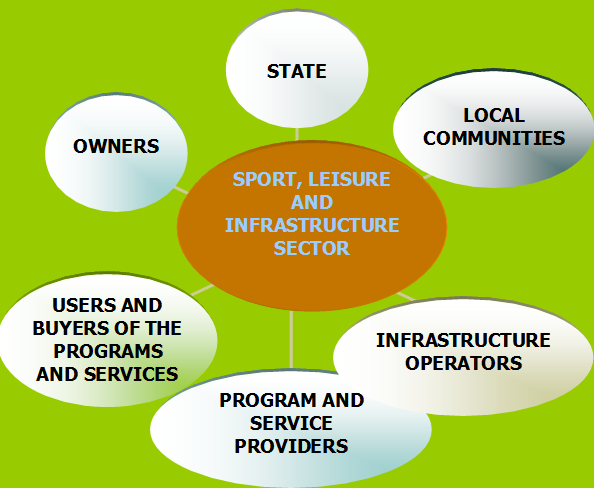
Public sector encompasses states, local communities, infrastructure operators, public institutions and enterprises at the local, regional and national level, sport and other associations. Sport and leisure infrastructure is mainly owned by local communities and operated by public operators. Public infrastructure operators ensure implementation of public interests, availability and quality of services for all people and safety. Public programs include physical education, sport for all, recreation, programs for children, youth, women, elderly people and special groups. Programs, services and use of infrastructure, are mainly free of charge or have low prices that are tailored to purchasing power of local population. Management of public sport and leisure infrastructure is in many cases rigid and bureaucratic. Political interests are very powerful and often do not reflect the needs of the population and financial possibilities. In public institutions there often are not enough management skills, technical knowledge and entrepreneurship, which provides constant inflow of new ideas and proposals for innovative programs and services, advanced technologies, more efficient management and maintenance. Main reasons for this situation are: insufficient implementation of public interests in the decision-making processes, illegally exercise of political interests, professionally incompetent management and non-stimulating business environment. In many cases we can find deficiency in effective control of public funding. Main responsibilities for sustainable development of sport and leisure infrastructure are on the side of the states and local communities, which are not qualified for taking long-term decisions. Professional institutions and experts are often not included in the decision making process. Thus formed, "white elephants", which are facilities that are not well accepted by local population, pollute and degrade natural and urban environment. They do not ensure sustainable development. Many such sport centers were built for "one event«. Operations and maintenance require too many organizational, human, material and financial resources, so they are often empty or closed. They represent huge problems and burdens for the owners and operators. Private sector includes owners and private firms. They own and operate tourism industry and infrastructure for leisure, which offer a wide range of tourist, sport and leisure programs and services. All programs and services are payable. The prices are often high, so their availability is limited. Private sector do not implement public interests. It is based on entrepreneurship. Owners are looking for profitable business opportunities. Management is professional, uses professional business skills and provides high quality of the services. Operations are more efficient than in public sector. Private sector is not directed towards sustainable development. It often has short-term interests in "easy earnings". There are also private "white elephants". They are results of bad business decisions, based on insufficient knowledge and experience. Private companies can bankrupt easier than public institutions. Social management encompasses public and private interests in the field of sport, leisure and infrastructure. It is public-private partnership. This is a rapidly growing sector, which includes new types of non-profit organizations with professional management. They meet public interests, while operating as professional enterprises. Supervisory bodies are composed of representatives of local authorities and civil society. They implement the interests of local communities, civil associations and population. Professional management ensures efficient operations, which generate profit that is reinvested in the infrastructure, new programs and services. Organizations have contracts and cooperate with local communities. They often function as centers or »clubs« that offer services to members for the membership fee and non-members for the payments of services. Programs are tailored to different groups of people, quality and purchasing power and include wide range of innovative sport, leisure, fitness, wellness and other services, promoting healthy life style. Prices are adjusted to the purchasing power of the local population. They employ mainly people from the local communities. Organizations are on the market, but operate as non-profit institutions supervised by municipalities and associations. Social management of sport, leisure and infrastructure, became an important part of economy in some countries and regions. Changes
Environmental changes, shrinking of natural resources, ageing of population and modern lifestyles, cause changes of infrastructure, sport and leisure programs.
New innovative programs have affect on the planning and construction of sport and leisure infrastructure. And vice versa. New environmentally friendly technologies, stimulate development of new programs and services.
Scheme 4: Changes in sport, leisure and infrastructure 
Future trends Environmental, economic and social changes, which already happened or will happen in the near future, will cause enormous changes in sport, leisure and infrastructure. Scheme 5: Future trends in sport, leisure and infrastructure 
Climate changes and excessive consumption of natural resources, will influence the economic situation and change sport and leisure. Countries, regions and local communities, will regulate legal status of the sport and leisure services providers and infrastructure operators. They will introduce new funding schemes of sport and infrastructure.
Climate changes and increasingly limited natural resources will have strong impact on the changed relations between construction of new facilities and reconstructions of existing infrastructure. Huge areas, water, energy and other resources, will not be available in the same way as they were in the past. Local communities and investors, will devote more attention to reconstructions and renewalls also due to restrictions placed by the international organizations. Existing facilities and centers are often completely neglected in deserted urban areas, for decades.
New technologies will be developed. They will ensure more rational use of water, energy and other resources, cut operating costs and introduce new materials, such as sport flooring, artificial turf and equipment, supporting development of new progams and more efficient utilization of infrastructure. These technologies will also reduce negative impacts on climate and biodiversity.
Economic changes will lead to changes in social structure. Urban population is growing and procentige of elderly people is increasing. Active working period is longer. There are large migrations between countries and regions. Social diverzification is bigger. Social changes will stimulate creation of the "new philosophy" of sport and leisure and development of new "innovative" programs and services. They will be more diversified and designed for target groups of users and customers; children, youth, women, elderly people and special groups. The programs will be focused on education, leisure, recreation, body shaping, rehabilitation and promotion of healthy life.
Social and economic changes will lead to new systems of social management, which will exercise public and private interests in sport, leisure and infrastructure. Greater emphasis will be placed on linking management and programs to local communities. Sport centers will be transformed in the centers (clubs) of local social life, offering wide variety of programs and services and employing local population.
Development of new programs and services and more efficient management, will stimulate design of new educational programs and professional training. Universities and business schools will develop specific programs of undergraduate and postgraduate education and training in the context of lifelong education.
Sport and leisure infrastructure will become increasingly multifunctional. It will be used for various commercial activities and diverse programs. Multipurpose facilities such as halls, stadiums, swimming pools and other facilities, new technologies, special equipment and innovative programs, will provide more effective operations, efficient utilization of infrastructure and marketing of programs. |
INFRASTRUCTURE
Sport, leisure and infrastructure
compose economic sector,
which includes planning, construction, management, maintenance and marketing
of facilities, systems and programs.
Sustainable development, management, new technologies and innovative programs
require professional managers and skilled workers.
|
1. General information about the program
1.1. Fields of education
Interdisciplinary educational program for jobs and professions, which are specific to managing sport, leisure and infrastructure, includes knowledge and business skills in planning, construction, management and maintenance of sport and leisure infrastructure and programs.
Program encompasses four fields of education: sustainable development, "social" management, infrastructure and programs.
Scheme 6: Fields of education
1.2. Objectives
Most important objective, are excellent skilled professionals and non-professional managers, who have knowledge and skills for development and marketing innovative programs and efficient operations of sport and leisure infrastructure and new technologies.
Program objectives are:
- 1.Development and implementation of under-graduate and post-graduate university programs.
- 2.Development and implementation of certified professional training programs for employees and officials of sport and leisure infrastructure operators, business associations, companies, municipalities and sport organizations.
- 3.New educational system, which will provide knowledge and business skills for effective infrastructure management and development of innovative sport and leisure programs.
1.3. Students
The program is aimed at students in under-graduate and post-graduate university programs, officials, managers and professionals in sport and leisure infrastructure operators, municipalities, ministries, sport organizations, companies and suppliers of goods and services.
1.4. Program structure Program is devided in two semesters, four educational fields, eight modules and 76 subjects. - 1.Sustainable development and infrastructure
- 1.1.Sustainable development
- 1.1.1.Sustainable development
- 1.1.2.Infrastructure planning
- 1.2.Infrastructure
- 1.2.1.Operations and maintenance
- 1.2.2.Communal and technological systems
- 2.Management and programs
- 2.1.Programs
- 2.1.1.Programs
- 2.1.2.Marketing
- 2.2.Management
- 2.2.1.Management
- 2.2.2.Business functions
1.5. Relations with other programs Program is linked to curriculums of Universities and business schools, which have included it in their under-graduate or post-graduate university studies or certified programs of professional training. Program is implemented also in the form of licensed seminars.
Educational program is an international program. International Association of sport and leisure infrastructure, has signed agreements with universities, business schools, professional institutions and companies in Europe and Latin America and Caribbean, for development, registration and implementation of the program.
Different formats of program differ in content (selection of subjects), extent (number of hours of lectures, pedagogical hours) and execution (study visits, examination).
1.6. Organization International Association of sport and leisure infrastructure is establishing educational center. This center will develop, promote, register and execute (in some cases) the program in cooperation with Universities, business schools, professional institutions and companies, international associations, sport organizations and operators of sport, leisure and infrastructure. 1.7. Consortium
IASLIM has formed Consortium of Universities, business schools, professional institutions, companies, sport and leisure infrastructure operators. Members of consortium are participating in development, promotion, registration and implementation of the program.
IASLIM is surching for new Consortium members in different continents, regions and countries. 1.8. Program Council Program Council directs all activities conneted with educational project. Members of the Council are experts, professionals and managers, who are appointed by the Consortium. 1.9. Professors and lecturers Lecturers are University professors, lecturers in specialized educational institutions and experts from professional institutions and companies, which operate in the sector of sport, leisure and infrastructure. 1.10. Number of students Estimated target group is several thousands students and managers. This number includes students in under-graduate and post-graduate University programs, and participants of certified professional training programs for managers, professionals, officials in employees of sport and leisure infrastructure operators, business associations, companies, municipalities and sport organizations. Estimated structure of students/participants: 50% - managers and professionals in sport and leisure infrastructure operators, 20% - officials in ministries, directorates and local municipalities, 10% - managers and employees in companies, suppliers of goods and services, 10% - officials in sport organizations and sportsmen and 10% - students at Universities and business schools. 1.11. Literature Literature consists of: (1) laws and regulations (planning, construction, management and maintenance of sport and leisure infrastructure, sport, leisure), (2) environmental standards, (3) technical standards, (4) study materials prepared by professors and lecturers, (5) referential scientific works and (6) professional literature in the field of sport, leisure and infrastructure. 2. Development, implementation and funding of the program 2.1. Development Program Council has developed basic structure and content of the program. It will be continously supplemented and changed in accordance with scientific discoveries, state-of-the-art technologies, program innovations, environment, social and economic changes.
Program Council will make selection of professors, speakers and experts, who will participate in development of the program.
Program will be adopted to specific environment, country or region by Universities, business schools and educational institutions, members of Consortium. Program will be translated in different languages. 2.2. Development costs
Costs of program development include: (1) scientific and expert work in developing structure and content of the program, (2) author's work in preparing content and study materials for subjects, (3) preparation of written examination, (4) preparation of study visits and (5) organizational structure of educational project.
2.3. Financial sources for development Development of program will be financed from: (1) public funding - Ministry of education and sport, (2) private funding - consortium members and partners and (3) sponsors and donors. 2.4. Program implementation costs Program implementation costs include: (1) organization and implementation of program, (2) lectures and exercises, (3) mentorship and councelling, (4) study visits and (5) examination. 2.5. Financial sources for implementation Program implementation will be funded from: (1) public funding - Ministry of education and sport, (2) tuition fees and (3) sponsors and donors. 3. Conditions for registration 3.1. Level of education
For registration in the program, students must fulfil different levels of education for different types of studies. Universities and business schools determine conditions for under-graduate and post-graduate studies.
Program Council will determine conditions of registration in certified professional training courses/programs.
4. Study programs 4.1. Forms of program Universities, business schools and other educational institutions, will decide on form of the program. Schools will include program in their curriculums as certificated professional training courses, under-graduate or post-graduate university studies. Schools will define content and size of different forms of the program. Programs will have the same basic structure. Different forms will differ in content and size: 1. Certified professional training courses (2 study years) 336 hours of lectures (672 pedagogical hours of study activities) 2. Under-graduate university studies (3 study years) 672 hours of lectures (1.344 pedagogical hours of study activities) 3. Post-graduate university studies (2 study years) 336 hours of lectures (672 pedagogical hours of study activities) Students in certified professional training courses at Universities, business schools and specialised educational institutions, can acquire professional title: - licenced manager of sport and leisure programs, - licenced manager of sport and leisure infrastructure.
Students in under-graduate programs at Universities and business schools, can acquire VII level of education and professional title:
- graduate manager of sport and leisure programs, - graduate manager of sport and leisure infrastructure. Students in post-graduate programs at Universities and business schools, can acquire VII level of education and professional title: - senior manager of sport and leisure programs, - senior manager of sport and leisure infrastructure, - senior adviser for sport and leisure infrastructure. 4.2. Advancement
Students will enter the program with required completed level of education. Students will acquire higher professional title in accordance with the Rules of Universities, business schools and specialised educational institutions.
4.3. Highest professional title in the program Highest professional title in the program is senior manager and senior adviser of sport and leisure programs / infrastructure. 5. Conditions for completion the program 5.1. Attendance at lectures 75% attendance at lectures is condition for registration for examination. 5.2. Examination Conditions to perform examination are required attendance at lectures and positively assessed (research) project. Exams are performed in program modules. Candidate has the right to three examinations. If candidate is not successful in three attempts, he must re-attend the program. 5.3. (Research) Projects Each semester student prepares two (research) projects in defined field of education, under supervision of mentor. Projects include: (1) definition of thesis, (2) review/analysis of circumstances/ situation, (3) proposals for confirmation or rejection of the thesis, (4) conclusions and (5) sources. Size of project is approximatelly one author's pole. 5.5. Study visits Each semester students attend two study visits to sport/tourist centers. Study visits include presentation of: (1) organizational structure, management and human resources, (2) facilities and technologies, (3) programs and services and (4) marketing. Students visit facilities, technological systems and programs. Study visits last from one to four days. 5.4. Diploma Students who successfully passed exams and defended diploma thesis, get diploma and professional title. 5.5. License For certifying licences, managers must attend licenced professional seminars, which are define in annual professional training program. |
6. Curriculum 6.1. Semesters Program has two semesters.
First semester is "Sustainable development and infrastructure." It includes two educational fields, four modules and 40 subjects. In certified professional training courses and post-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 176 hours of lectures (528 pedagogical hours of study activities). In under-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 352 hours of lectures (1.056 pedagogical hours of study activities). Students prepare two research projects and attend two study visits.
Second semester is "Management and Programs." It includes two educational fields, four modules and 36 subjects. In certified professional training courses and post-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 160 hours of lectures (480 pedagogical hours of study activities). In under-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 320 hours of lectures (960 pedagogical hours of study activities). Students prepare two research projects and attend two study visits.
6.2. Fields of education Educational program encompasses four fields of education, which represents basic structure of the program. First educational field is "Sustainable development". It includes two modules and 17 subjects. In certified professional training courses and post-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 80 hours of lectures (240 pedagogical hours of study activities). In under-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 160 hours of lectures (480 pedagogical hours of study activities). Students prepare one research project and attend study visit. Educational field includes sustainable development and infrastructure planning. Second educational field is "Infrastructure". It includes two modules and 23 subjects. In certified professional training courses and post-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 96 hours of lectures (288 pedagogical hours of study activities). In under-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 192 hours of lectures (576 pedagogical hours of study activities). Students prepare one research project and attend study visit. Educational field includes infrastructure operation and maintenance and communal and technological systems. Third educational field is "Management". It includes two modules and 17 subjects. In certified professional training courses and post-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 80 hours of lectures (240 pedagogical hours of study activities). In under-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 160 hours of lectures (480 pedagogical hours of study activities). Students prepare one research project and attend study visit. Educational field includes management and business functions. Fourth educational field is "Programs". It includes two modules and 19 subjects. In certified professional training courses and post-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 80 hours of lectures (240 pedagogical hours of study activities). In under-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 160 hours of lectures (480 pedagogical hours of study activities). Students prepare one research project and attend study visit. Educational field includes programs and marketing. 6.3. Program modules Program encompasses eight modules, which represent round up program areas. First program module is »Sustainable development«. It includes 9 subjects. In certified professional training courses and post-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 40 hours of lectures (120 pedagogical hours of study activities). In under-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 80 hours of lectures (240 pedagogical hours of study activities). Semester 1: Sustainable development and infrastructureField of education 11: Sustainable developmentModule 111: Sustainable development Subject 11101 Sport philosophy and ethics Subject 11102 Sustainable development Subject 11103 Impact of infrastructure on the environment Subject 11104 Climate changes and future development of sport and leisure infrastructure Subject 11105 Social changes and future development of sport and leisure infrastructure Subject 11106 Olympic movement and sustainable development of sport Subject 11107 Public interests in sport and infrastructure Subject 11108 Public-private partnership in sport, leisure and infrastructure Subject 11109 The future of leisure, sport and infrastructure Second program module is »Infrastructure planning«. It includes 8 subjects. In certified professional training courses and post-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 40 hours of lectures (120 pedagogical hours of study activities). In under-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 80 hours of lectures (240 pedagogical hours of study activities). Semester 1: Sustainable development and infrastructureField of education 11: Sustainable developmentModule 112: Infrastructure planning Subject 11201 Regional planning of the sport centers Subject 11202 Urban planning of the sport centers Subject 11203 Architectural design of sport facilities Subject 11204 Standards and regulations of planning and building of sport and leisure infrastructure Subject 11205 National, regional and local networks of sport and leisure centers Subject 11206 Sustainable development of sport centers and facilities Subject 11207 Reconstruction of sport facilities Subject 11208 Future trends in the infrastructure planning Third program module is »Operations and maintenance«. It includes 11 subjects. In certified professional training courses and post-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 48 hours of lectures (144 pedagogical hours of study activities). In under-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 96 hours of lectures (288 pedagogical hours of study activities). Semester 1: Sustainable development and infrastructureField of education 12: InfrastructureModule 121: Operations and maintenance Subject 12101 Sport and leisure infrastructure Subject 12102 Standards and regulations of management and maintenance of sport and leisure infrastructure Subject 12103 Arenas Subject 12104 Swimming pools Subject 12105 Athletic and football stadiums Subject 12106 Ice rings Subject 12107 Ski slopes and ropeways Subject 12108 Golf courses Subject 12109 Other sport facilities Subject 12110 School sport facilities Subject 12111 Sport playgrounds for children Fourth program module is »Communal and tehcnological systems«. It includes 12 subjects. In certified professional training courses and post-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 48 hours of lectures (144 pedagogical hours of study activities). In under-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 96 hours of lectures (288 pedagogical hours of study activities). Semester 1: Sustainable development and infrastructureField of education 12: InfrastructureModule 122: Communal and technological systems Subject 12201 Communal and traffic systems Subject 12202 Water supply systems Subject 12203 Energy supply systems Subject 12204 Natural air treatment systems Subject 12205 Heating systems and indoor air treatment technologies Subject 12206 Water treatment technologies Subject 12207 Hazardous substances and material management Subject 12208 Waste management Subject 12209 Cleaning services Subject 12210 Communication systems Subject 12211 Lightning and acoustic technologies Subject 12212 Safety systems Fifth program module is »Programs«. It includes 10 subjects. In certified professional training courses and post-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 40 hours of lectures (120 pedagogical hours of study activities). In under-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 80 hours of lectures (240 pedagogical hours of study activities). Semester 2: Programs and management Field of education 21: ProgramsModule 211: Programs Subject 21101 Programs and services Subject 21102 Sport for all Subject 21103 Profesional sport Subject 21104 Fitness in wellness programs Subject 21105 Tourist programs Subject 21106 Events Subject 21107 Special programs Subject 21108 School sport education Subject 21109 Programs for children and youth Subject 21110 Accommodations, catering, VIP, medical and other services Sixth program module is »Marketing«. It includes 9 subjects. In certified professional training courses and post-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 40 hours of lectures (120 pedagogical hours of study activities). In under-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 80 hours of lectures (240 pedagogical hours of study activities). Semester 2: Programs and management Field of education 21: ProgramsModule 212: Marketing Subject t 21201 Tourism, leisure and sport market Subject 21202 Satisfying buyers' and users' needs Subject 21203 Market research Subject 21204 Marketing strategies Subject 21205 Marketing program Subject 21206 Psihology of market communication Subject 21207 Brands and integrated communications Subject 21208 Marketing and »Live TV« Subject 21209 Event management Seventh program module is »Management«. It includes 8 subjects. In certified professional training courses and post-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 40 hours of lectures (120 pedagogical hours of study activities). In under-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 80 hours of lectures (240 pedagogical hours of study activities). Semester 2: Programs and management Field of education 21: ManagementModule 211: Management Subject 211101 Fundamentals of management Subject 21102 Comprehensive strategic analysis Subject 21103 Development strategy Subject 21104 Organizational structures and proceses Subject 21105 Project management Subject 21106 Organizational culture Subject 21107 Change management Subject 21108 Crisis management Eight program module is »Business functions«. It includes 9 subjects In certified professional training courses and post-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 40 hours of lectures (120 pedagogical hours of study activities). In under-graduate university studies, the program encompassess 80 hours of lectures (240 pedagogical hours of study activities). Semester 2: Programs and management Field of education 22: ManagementModule 222: Business functions Subject 22201 Business economics Subject 22202 Business plan Subject 22203 Purchasing management Subject 22204 Sales management Subject 22205 Profit and nonprofit management Subject 22206 Financing of infrastructure Subject 22207 Risk management, business planning and control Subject 22208 Human resource management and team building Subject 22209 Health and safety management Conclusion
International School of Sport and Leisure Infrastructure Management is new comprehensive interdisciplinary educational program. It will be supplemented by Universities, business schools and specialized educational institutions and incorporate in their curriculums. Schools will offer the program as certified professional training programs, under-graduate or post-graduate university studies. The needs for such education and professional training are big.
Jože Jenšterle Secretary General |
|
